Wi-Fi has transitioned from a novel technology to an indispensable utility, profoundly impacting how individuals, businesses, and communities connect and operate in the modern world. Its widespread adoption underscores its critical importance across virtually every facet of daily life.
Wireless Access Points(WAPs) are key to providing wireless Wi-Fi connectivity for internet users in various settings such as homes, offices, educational institutions, commercial/Industrial hubs and public infrastructure. They eliminate the constraints of physical cables, offering significant flexibility and convenience.
Essentially, Wireless Access Point(WAPs) functions as a bridge, facilitating the bidirectional conversion between wireless and wired signals.
WAPs offer a multitude of advantages:
- Extended Coverage: They significantly expand the reach of a wireless network, allowing devices to connect reliably from greater distances than with a router alone.
- Enhanced Network Performance: By distributing network traffic across multiple access points, WAPs alleviate congestion and contribute to a more stable and efficient network.
- Advanced Security: WAPs incorporate robust security features, including various encryption protocols, to safeguard the network against unauthorized access.
- Seamless Roaming: They facilitate uninterrupted connectivity by allowing devices to smoothly transition between different access points without dropping the connection.
Furthermore, WAPs, along with mesh extenders, can be deployed to broaden the signal range and strengthen a wireless network, effectively eliminating “dead spots” and ensuring comprehensive wireless coverage, particularly in larger buildings or office spaces. The settings of multiple WAPs can often be centrally managed from a single device, simplifying network administration.
In both personal and professional settings, wireless access points are indispensable for providing the necessary connectivity and flexibility to maintain device productivity and seamless network access.
SCENARIO BASED SOLUTIONS
Wi-Fi Network Solutions for Residential Homes, Small Businesses Offices and Retail Space
Residential homes, small business offices and retail space Wifi network solutions encompass a set of technologies and components to provide efficient and reliable networking capabilities.
Key elements include
- Wireless Routers: These are a good starting point for most home and small office needs, offering a balance of performance and ease of use.
- Wireless Access Point Systems: An access point is a device that allows you to connect wirelessly to a network, such as the internet. It acts as a bridge between your devices and the network, providing a wireless connection for your devices to access the network resources. Recommended for larger homes or offices that require extensive and consistent WiFi coverage across multiple rooms or floors, as they use multiple interconnected nodes to create a single, seamless network
- Mesh Wi-Fi Systems: Wi-Fi mesh network consists of multiple interconnected Wi-Fi devices, often called “nodes” or “satellite units,” that work together to form a single, unified network. One node acts as the primary router connected to the internet, while the others communicate wirelessly with each other and the main router to create a wide, seamless web of coverage.
- SIM card LTE Mobile Routers: Ideal for situations where wired internet is unavailable or for businesses that require flexible, mobile internet access with the ability to connect multiple devices.
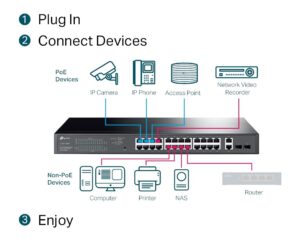
- Network Switches: Network switches often include features like power over ethernet (PoE), which allows them to power devices like access points and security cameras, and advanced management capabilities. They can also be used in more complex network architectures like spine-leaf topologies in data centers.
The aim is to deliver seamless connectivity, security, and flexibility for homes and small businesses, with user-friendly configuration and management options.
Industrial and Infrastructure Enterprise Level Wi-Fi Network Solutions
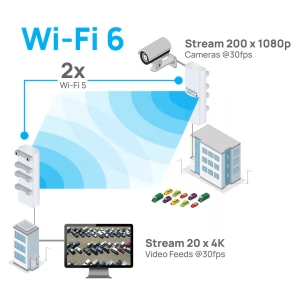
Industrial Level Wireless Access Point Network Solutions are designed to provide robust, reliable, and secure wireless connectivity in demanding industrial environments, often integrating with existing wired infrastructure and supporting the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). These solutions leverage advanced Wi-Fi standards like Wi-Fi 6 & 7 to deliver high speeds and low latency, and employ features like Access Point networking, strong security protocols and ruggedized hardware to withstand harsh conditions.
Key elements include
- Harsh Environment Resilience:
Industrial Wi-Fi products are built with robust designs to mitigate downtime caused by environmental factors such as extreme temperatures, shock, vibration, and electromagnetic interference (EMI). - Enhanced Performance:
Modern industrial Wi-Fi, particularly Wi-Fi 6 & 7, offers high speeds (e.g., exceeding Gigabit), improved data rates, and efficient data transmission for demanding IIoT applications. Features like MU-MIMO and OFDMA improve performance in congested areas. - Reliability and Redundancy:
Utilize self-forming and self-healing capabilities to ensure continuous connectivity. Industrial switches with features like Ethernet Ring Protection Switching can also enhance network robustness. - Flexibility and Scalability:
Industrial wireless solutions support various configurations, including mesh networks, and can seamlessly integrate with wired networks, providing flexible deployment options for diverse industrial applications. - Management and Monitoring:
Management suites allow for wireless visibility and management within industrial environments.
Their purpose is to enhance efficiency, safety, and operational effectiveness in sectors such as manufacturing, energy, transportation, and utilities.
Our Network Products
Our Network Products Varieties
Sin Chew Alarm provides a wide array of Network Products to meet Scenarios-Specific needs
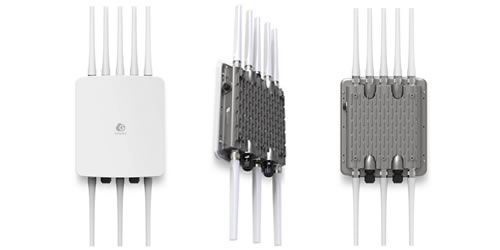
Indoor Wireless Access Points
Wi-Fi is no longer a luxury but a necessity for homes, offices, and public venues alike.
Indoor access points are designed with aesthetics and discrete placement in mind, often featuring sleek designs that blend into their surroundings. Beyond their appearance, their primary function is to optimize wireless coverage, capacity, and performance within enclosed spaces.
Indoor access points are indispensable across a wide range of indoor settings:
Residential Homes: Extending Wi-Fi coverage to large homes, multi-story houses, or properties with architectural obstacles.
Office Buildings: Providing reliable and high-performance Wi-Fi for employees, guests, and IoT devices in corporate environments, co-working spaces, and branch offices.
Educational Institutions: Ensuring seamless connectivity for students and staff in classrooms, libraries, dormitories, and common areas.
Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities: Supporting wireless medical equipment, patient monitoring systems, and providing internet access for patients and staff.
Retail and Hospitality: Offering guest Wi-Fi in shops, restaurants, cafes, and hotels, enhancing customer experience and supporting point-of-sale systems.
Warehouses and Manufacturing: Enabling wireless communication for inventory management, automated systems, and personnel in industrial settings.
Outdoor Wireless Access Points
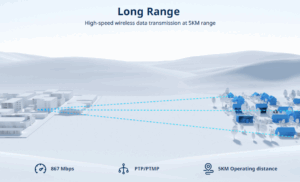
Outdoor Access Points (APs) are purpose-built to extend reliable and robust wireless networks into open-air environments. These specialized devices are engineered to withstand the rigors of nature, delivering high-performance Wi-Fi to a myriad of outdoor settings, from sprawling campuses and public parks to industrial facilities and smart city deployments.
The fundamental difference between indoor and outdoor APs lies in their resilience and design. Outdoor APs are housed in rugged, weatherproof enclosures, protecting their sensitive electronics from extreme temperatures, heavy rain, snow, dust, and even direct sunlight. This robust construction, often accompanied by high IP (Ingress Protection) ratings (e.g., IP65, IP67, IP68), ensures continuous and stable operation in challenging environmental conditions
Outdoor access points are essential for a diverse array of outdoor scenarios:
Campus Networks: Extending Wi-Fi coverage across university campuses, school grounds, and corporate parks, connecting outdoor spaces, sports fields, and remote buildings.
Hospitality and Resorts: Offering seamless Wi-Fi connectivity around pools, outdoor dining areas, gardens, and other recreational spaces.
Industrial and Manufacturing Facilities: Enabling wireless communication for IoT devices, automated machinery, security cameras, and personnel in outdoor industrial zones, warehouses, and construction sites.
Smart City Initiatives: Serving as a backbone for smart city applications, supporting sensors, public safety systems, environmental monitoring, and connected street furniture.
Sporting Venues and Arenas: Providing high-density Wi-Fi for spectators, media, and operational staff in outdoor stadiums, concert venues, and event spaces.
Surveillance Systems: Powering and connecting outdoor IP cameras for security and monitoring purposes.
Wireless Bridge
A wireless bridge is a networking device that creates a wireless connection between two or more wired network segments, effectively acting as an invisible Ethernet cable, connecting networks where cables can’t.
Wireless bridges are invaluable in various scenarios where traditional wired connections are unfeasible or uneconomical.
Wireless bridges are invaluable in various scenarios where traditional wired connections are unfeasible or uneconomical:
Connecting Multiple Buildings: Linking separate buildings on a campus, in an industrial park, or even across a street to share a single internet connection or internal network resources.
Extending Network to Remote Structures: Providing network access to sheds, garages, guest houses, or barns located far from the main building.
Temporary Network Deployments: Setting up quick and temporary network links for events, construction sites, or disaster relief efforts.
Backhauling Surveillance Systems: Transmitting high-definition video feeds from IP cameras located at remote perimeters back to a central monitoring station.
Industrial Automation: Connecting industrial equipment and sensors across large factory floors or outdoor operational areas where running cables is difficult.
Rural Broadband Extension: In some cases, wireless bridges are used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to deliver broadband services to remote or underserved areas.
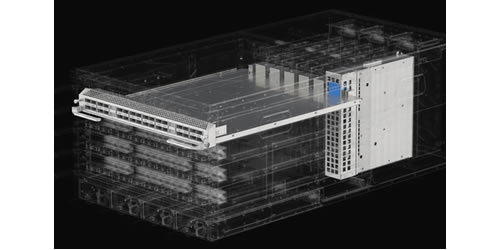
Network Switch
Network Switches are highly intelligent traffic controller, responsible for directing data packets efficiently and ensuring smooth communication between all connected devices.
Network switches come in various forms and with different capabilities to suit diverse networking needs:
By Management Capability:
Unmanaged Switches: These are the simplest and most cost-effective. They offer plug-and-play functionality with no configuration required. Ideal for basic home networks or small offices where simplicity is paramount.
Managed Switches: These offer a wealth of features for network administrators to control and monitor network traffic. They provide capabilities like Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs), Quality of Service (QoS), Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), port mirroring, and extensive monitoring tools. Managed switches are essential for larger, more complex, and security-conscious networks.
Smart/Web-Managed Switches (Lightly Managed): A middle ground between unmanaged and fully managed switches. They offer some basic management features (often via a web interface) but lack the deep configuration options of fully managed switches. Suitable for small to medium-sized businesses looking for more control without the complexity of enterprise-grade managed switches.
By Power Delivery:
Power over Ethernet (PoE) Switches: These switches can deliver electrical power along with data over standard Ethernet cables. This simplifies the deployment of devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, wireless access points, and IoT sensors, as they don’t require separate power outlets. PoE+ (802.3at) and PoE++ (802.3bt) standards offer higher power budgets for more demanding device
By Speed:
Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps): Increasingly rare in new deployments, but still found in older infrastructure.
Gigabit Ethernet (1 Gbps): The most common standard today for local area networks, offering ample bandwidth for most applications.
Multi-Gigabit Ethernet (2.5 Gbps, 5 Gbps): Bridging the gap between 1 Gbps and 10 Gbps, useful for modern high-bandwidth wireless access points and demanding workstations.
10 Gigabit Ethernet (10 Gbps) and beyond: Used for server uplinks, data center backbone connections, and high-performance computing environments.
Frequently Asked Questions About WiFi Solutions in Singapore
How do you eliminate WiFi dead zones?
Several effective strategies can be used to eliminate frustrating WiFi dead zones in your home or business. We often recommend strategically deploying wireless access points to extend coverage seamlessly throughout your property. For larger residences or multi-story buildings, mesh WiFi solutions create a unified network with multiple nodes working together to blanket your space in a strong, consistent connection. Also, our expert technicians conduct thorough site surveys to identify problem areas and determine the optimal placement of equipment, ensuring a reliable WiFi system without weak spots.
What is the difference between routers and access points?
A router and a wireless access point serve different but often complementary roles in a network. A router, for instance, acts as the central hub, managing the connection between your network and the Internet. It also assigns IP addresses, handles network traffic, and often includes security features.
A wireless access point, on the other hand, primarily focuses on extending wireless coverage within an existing network. It connects to the router via an Ethernet cable and broadcasts a WiFi signal, allowing more devices to connect wirelessly. Sin Chew Alarm strategically utilizes both routers and access points to create comprehensive and efficient WiFi solutions in Singapore.
Which is better, a WiFi extender or mesh?
In many scenarios, a mesh WiFi system offers a superior solution compared to traditional WiFi extenders. While both aim to improve wireless coverage, mesh systems create a single, unified network where multiple nodes communicate seamlessly. This design allows for smoother transitions as you move around your property and often provides more consistent speeds. In contrast, extenders typically create a separate network, which can lead to dropped connections and reduced bandwidth. At Sin Chew Alarm, we often recommend mesh WiFi solutions for comprehensive and reliable whole-home or large office coverage
How much does it cost to get WiFi in a house?
The cost of setting up WiFi in a house in Singapore can vary depending on several factors. These typically include the internet service provider’s monthly subscription fees, which are influenced by the desired bandwidth and data plan. Additionally, the cost of equipment such as the router and any wireless access points or mesh components will factor into the initial setup expenses. More comprehensive WiFi solutions, designed for larger homes or with advanced features, may also involve higher upfront and recurring costs.